Ever wondered how your favorite animated movies, TV shows, and video games come to life? The magic happens inside an animation studio, where teams of talented artists, animators, and technicians work together to craft stunning visuals and compelling stories.
The process is complex, requiring multiple stages of planning, creation, and refinement before a finished product reaches the audience. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the entire animation production process, from the initial idea to the final render.
The Animation Production Process
Pre-Production: Laying the Foundation
Before any animation is created, the groundwork must be set. Pre-production involves planning, conceptualizing, and organizing every aspect of the project to ensure efficiency and creative clarity.
Key Steps in Pre-Production:
- Idea Development & Scriptwriting: Writers and directors brainstorm ideas, develop characters, and create a compelling script. This is the foundation of every animated project.
- Storyboarding: Artists create visual representations of scenes to plan the sequence and framing of the story, much like a comic book layout.
- Concept Art & Character Design: Designers sketch characters, environments, and objects to establish the visual style. They refine these sketches based on feedback from the creative team.
- Animatics: A rough animated version of the storyboard helps determine pacing and scene transitions, ensuring the narrative flows smoothly.
- Voice Casting & Recording: Professional voice actors bring characters to life, recording dialogue that animators will later sync with characters’ mouth movements.
- Technical Planning: Decisions about animation techniques, rendering styles, and software tools are made at this stage to streamline the production process.
Production: Bringing Art to Life
Once pre-production is complete, the real animation work begins. This is where the visuals start taking shape, with various teams handling different aspects of production.
Key Steps in Production:
- Modeling: 3D animators create digital models of characters, props, and environments. In 2D animation, this stage involves drawing assets and backgrounds.
- Rigging: Characters are equipped with a skeletal structure to allow movement. In 3D animation, rigs determine how a character moves and interacts with objects.
- Animation: Frame-by-frame motion is created, making characters move realistically. This is one of the most time-consuming yet rewarding aspects of animation.
- Texturing & Shading: Surfaces are given color, patterns, and materials to make them look realistic and match the intended visual style.
- Lighting & Camera Work: Just like in live-action films, lighting and camera angles play a crucial role in creating atmosphere and guiding the viewer’s focus.
- Background & Environment Creation: Artists craft detailed backgrounds and environments, ensuring they match the mood and setting of the story.
Post-Production: Perfecting the Animation
After the core animation is completed, finishing touches are added to enhance the visual and auditory experience, ensuring the final product is polished and ready for distribution.
Key Steps in Post-Production:
- Compositing: Combining different elements like characters, effects, and backgrounds into a cohesive scene, blending everything seamlessly.
- Visual Effects (VFX): Adding special effects like explosions, fire, smoke, or magical elements to enhance storytelling.
- Sound Design & Music: Background music, sound effects, and final voice mixing bring scenes to life, adding emotional depth and immersion.
- Rendering: The final frames are processed to create high-quality visuals, requiring powerful computing resources and precise optimization.
- Editing & Final Cut: Editors assemble everything into a seamless story, ensuring smooth transitions, pacing, and coherence.
Animation Techniques Used in Studios
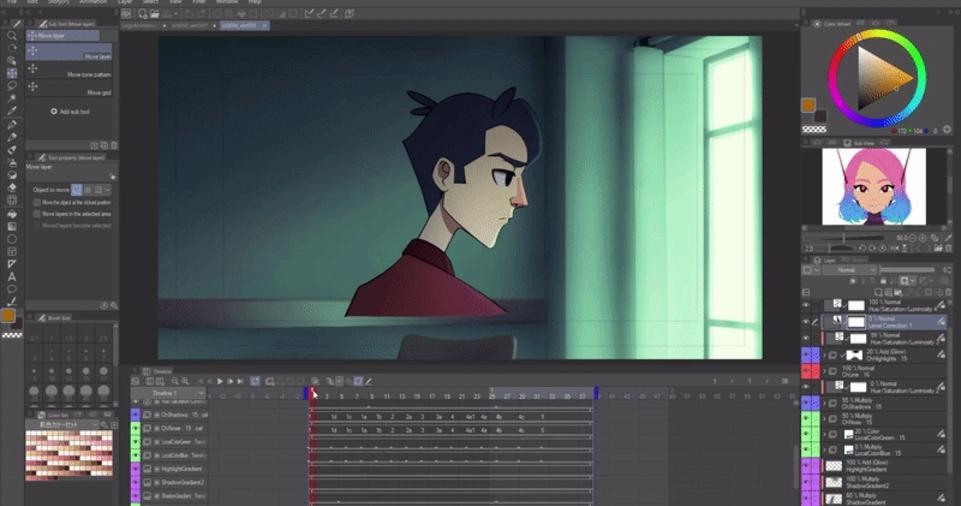
Different studios use various animation styles based on the project’s needs. Here are some popular methods:
| Animation Type | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 2D Animation | Hand-drawn or digitally animated characters & backgrounds | TV shows, commercials, explainer videos, mobile games |
| 3D Animation | Computer-generated characters & environments with depth and realism | Movies, video games, architectural visualization, advertisements |
| Stop Motion | Frame-by-frame photography of physical models or puppets | Claymation, indie films, special effects, TV ads |
| Motion Capture | Recording real-life movements and applying them to digital characters | Video games, realistic CGI films, sports analysis |
| Hybrid Animation | Combination of different techniques for a unique aesthetic | Modern animated films, mixed media projects |
ALSO READ:How to Use Basic Digital Tools for Animation (Without Professional Gear)
Case Study: Pixar’s Animation Pipeline
One of the most well-known animation studios, Pixar, follows a meticulous pipeline for its films. Their process includes:
- Story Development: Creating a script with deep emotional resonance, often taking years to perfect.
- Art & Design: Developing highly detailed characters and worlds, ensuring a consistent visual style.
- Animation & Rendering: Using cutting-edge technology to achieve realistic motion and textures.
- Final Editing & Post-Production: Fine-tuning every frame to perfection with compositing, VFX, and music scoring.
- Quality Control & Audience Testing: Pixar rigorously tests its films with audiences before release, making adjustments based on feedback.
Pixar’s dedication to storytelling and technology has led to timeless classics like Toy Story, Finding Nemo, and Inside Out.
Practical Tips for Aspiring Animators
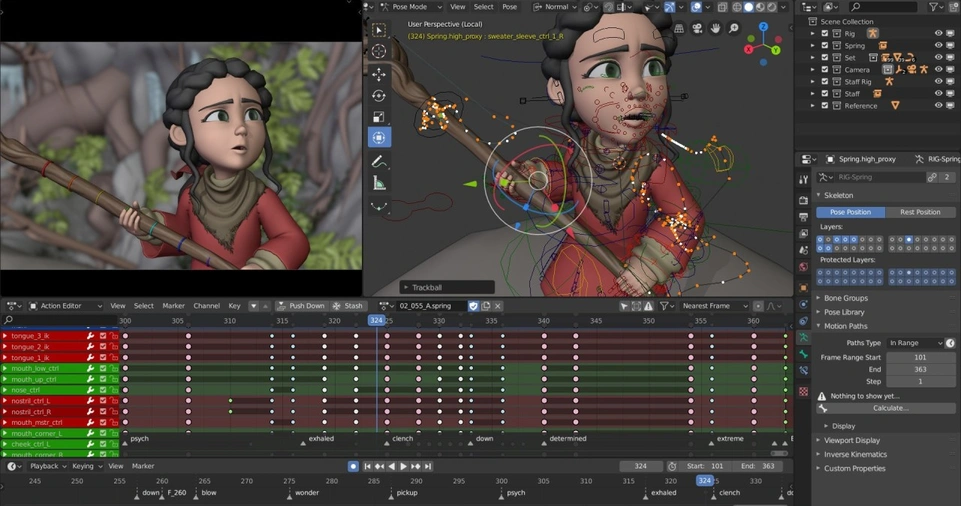
If you’re interested in working in an animation studio, here are some actionable tips:
- Learn Animation Software: Master industry-standard tools like Autodesk Maya, Blender, Adobe After Effects, and Toon Boom Harmony.
- Build a Strong Portfolio: Showcase your best work, including character designs, storyboards, and short animations. A well-curated portfolio is essential for job applications.
- Network with Professionals: Join online animation communities, attend industry events, and seek mentorship from experienced animators.
- Develop Storytelling Skills: Animation is about more than just visuals; strong storytelling can set your work apart.
- Keep Practicing & Stay Updated: Animation techniques and software evolve rapidly, so continuous learning is key to staying competitive.
ALSO READ:Mobile Animation Made Easy: 5 Powerful Apps for Creative Success
Conclusion
Animation studios are creative powerhouses where artistry and technology combine to produce breathtaking visuals. Whether you’re a fan of animated films or aspiring to enter the industry, understanding the production process can deepen your appreciation for this art form.
What’s Next?
If you’re excited about animation, why not start your own project? Try making a short animation using free software like Blender and explore online tutorials to develop your skills.

